Pus Cells in Urine
Pus Cells in Urine, The human body is a complex system, and its various functions are interconnected. One essential aspect of our health often overlooked is the condition of our urine. Pus cells in urine, though microscopic, can provide significant insights into our well-being. In this article, we’ll delve into what pus cells are, why they might appear in urine, and what steps can be taken for a healthier urinary tract.
Introduction:
Understanding the nuances of pus cells in urine goes beyond a routine checkup. It involves grasping the significance of these cells, their potential causes, associated symptoms, and the actions one can take for optimal urinary health.
What are Pus Cells?
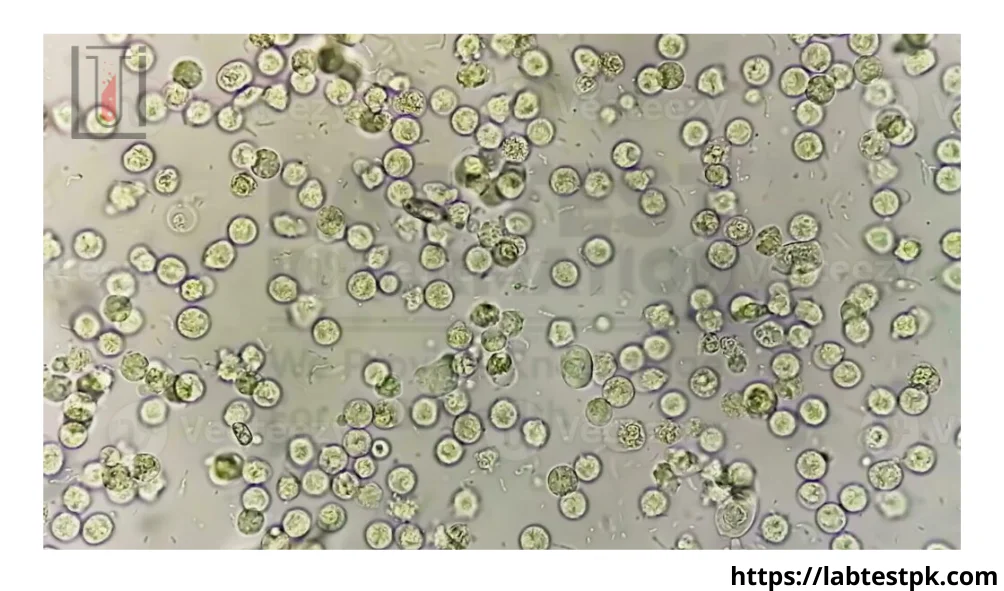
Pus cells, also known as pyuria, are white blood cells that accumulate in response to an infection or inflammation. In urine, their presence may indicate an underlying issue within the urinary tract. Normally, urine contains a small number of pus cells, but elevated levels can signal a problem.
Causes of Elevated Pus Cells
Various factors can lead to an increase in pus cells in urine. Infections, whether bacterial or fungal, are common culprits. Inflammation from injuries or trauma can also contribute to higher pus cell counts.
Symptoms Associated with Pus Cells in Urine
Recognizing symptoms associated with elevated pus cells is crucial. Pain during urination, changes in urine color or odor, and other signs should prompt further investigation into one’s urinary health.
Diagnostic Methods
To accurately diagnose the presence of pus cells, healthcare professionals employ urine analysis and microscopic examination. Additional tests may be recommended based on initial findings.
Common Conditions Leading to Pus Cells
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney infections, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common conditions associated with increased pus cells in urine. Understanding these conditions is essential for effective management.
Treatment Options
Addressing the root cause is key to treating pus cells in urine. Antibiotics, lifestyle changes, and follow-up care may be part of the recommended treatment plan.
Prevention Tips
Preventive measures play a crucial role in maintaining urinary health. Staying hydrated, practicing good personal hygiene, and adopting safe sexual practices are integral to preventing issues related to pus cells in urine.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Persistent symptoms or recurrent pus cells in urine should not be ignored. Seeking medical attention promptly can prevent the escalation of potential health issues.
Complications of Ignoring Pus Cells
Neglecting the presence of pus cells can lead to complications such as the spread of infection, kidney damage, and long-term consequences. Early intervention is vital.
Myth Busting: Common Misconceptions
Dispelling myths and misconceptions about pus cells in urine is essential for fostering a better understanding of urinary health. Clearing up misinformation can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their well-being.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Urinary Health
Simple lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments, regular exercise, and stress management, can contribute significantly to improved urinary health.
Pus Cells in Children’s Urine
Children may experience pus cells in their urine due to specific factors. Understanding these considerations and implementing appropriate treatments are crucial for pediatric urinary health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pus cells in urine serve as a valuable indicator of urinary health. Proactively understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments associated with elevated pus cells empowers individuals to take charge of their well-being. Prioritizing urinary health is a fundamental step toward maintaining overall health and vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can pus cells in urine go away on their own? Pus cells may reduce on their own, but persistent symptoms warrant medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Are all urinary tract infections (UTIs) associated with pus cells in urine? While not all UTIs cause an increase in pus cells, they are a common indicator of infection.
- Can lifestyle changes alone eliminate pus cells in urine? Lifestyle changes can contribute to urinary health, but professional guidance is essential for comprehensive management.
- Are there specific foods that worsen pus cells in urine? Some foods may exacerbate urinary issues, but a balanced diet is generally recommended for overall health.
- Is the presence of pus cells always a sign of a serious health issue? While elevated pus cells can indicate an underlying problem, not all cases are severe. Consultation with a healthcare professional provides clarity.

[…] urinary tract consists of structures like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and each of these structures is lined with epithelial cells. […]