Ferritin Level
Ferritin Level, A Ferritin test helps your doctor understand how much iron your body stores. A ferritin test measures the level of ferritin in your blood. Ferritin is a protein that stores iron inside your cells. you need iron to make healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. Iron is also important for healthy muscles, bone marrow, and organs including the brain. Ferritin acts as the reverse of iron in the liver and bone marrow
the more ferritin in your blood, the more stored iron your body which is toxic, and when low that is not good for the body. The concentration of ferritin in plasma is proportional to the amount of stored iron, therefor the measurement of plasma ferritin is the best f indicator of iron deficiency. Ferritin is what’s known as an acute phase reactant. It means body. experiences inflammation, ferritin levels will go up.
Storage site In Body:
The greatest concentrations of ferritin are typically in the cells of the liver (known as hepatocytes) and immune system (known as reticuloendothelial cells).
The normal value of Ferritin:
The normal value of ferritin test in blood:
- 12 to 150 ng/mL for females
- 12 to 300 ng/mL for males
Causes Of Low Ferritin blood:
- Excessive menstrual cycle
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Heart failure
- Tinnitus
- Leg Pain
- Dizziness, weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Arrhythmia (problem with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat)
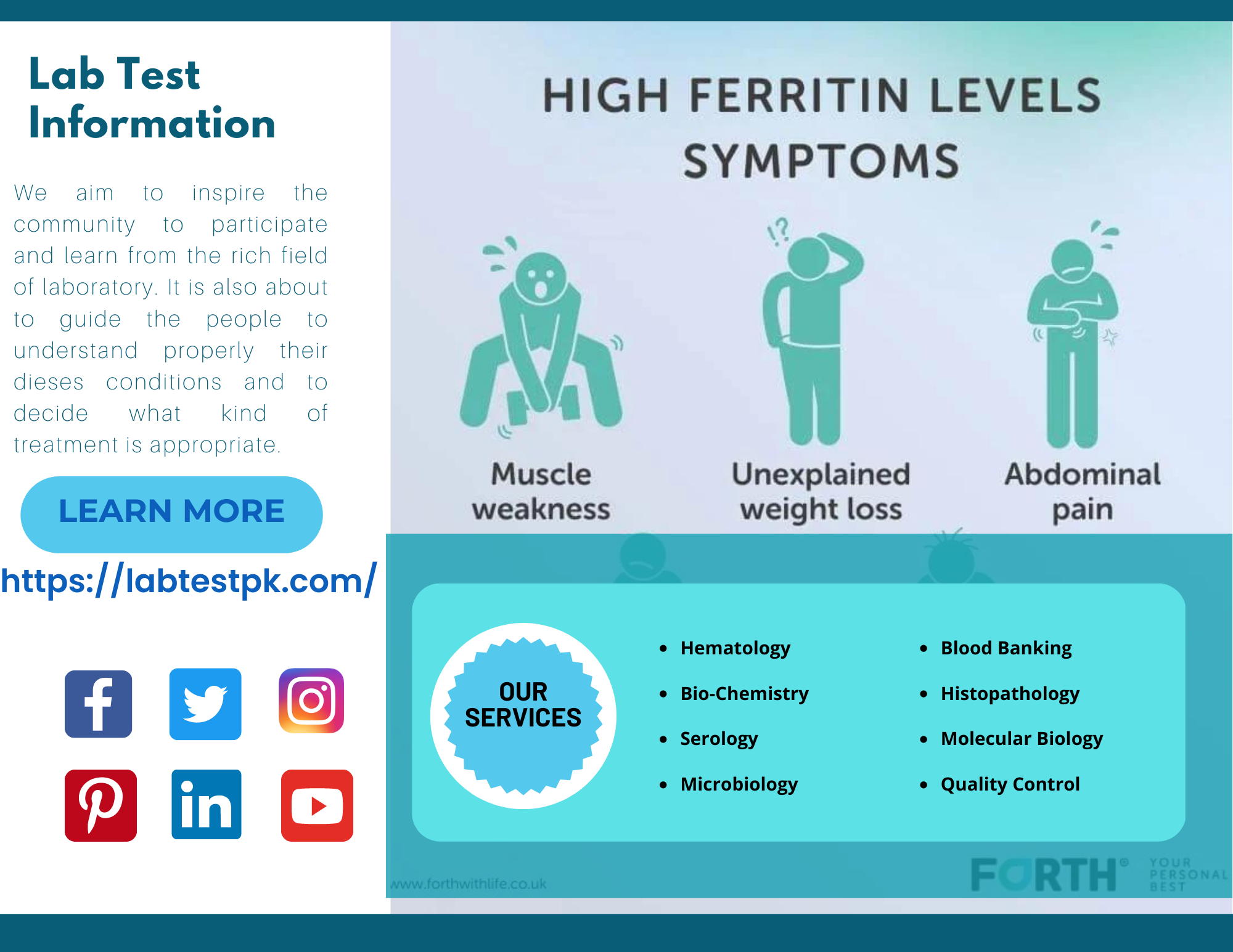
Causes of High Ferritin in Blood:
- Joint Pain, commonly in the knee by hands
- Loss of interest in sex or erectile dysfunction (ED)
- change in skin color
- Unexplained fatigue
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Chest Pain
- Heart Palpitation
- Stomach Pain
- Liver Damage
- Spleen Damage
- Alcohol Abuse
- Over Active Thyroid
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Weight loss
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Abdominal Pain

What is it used for:
Ferritin test is used to help check you’re is on levels. If your body is storing the right amount of iron & stay healthy. The test may also be used to:
- Hemochromatosis (called iron overloaded)
- Anemia (lack of iron in the blood)
- Liver Disease (much ferritin stored in the liver)
- Restless legs syndrome (tingling burning feeling in the leg)
- Adult still disease (pain, fever, rash)
- Monitor chronic (long-lasting Cancer, kidneys, and autoimmune disease)
Prepare for the Test:
AT fasting Condition for 12 hours before test Blood Sample required.
Procedure:
Collect 3 to 5ml blood in a Green Top or Gel Tube. Centrifuge the blood sample and separate the serum. After centrifugation serum is used for test and running for an advanced analyzer.

I’d love to be a part of group where I can get advice from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know. Thank you.
[…] mediastinal, Para-aortic). It involves a single group of nodes spread to automatically contiguous lymphoid tissue. The lymph system is made up of tissues and organs that produce, store, and carry white blood […]