Typhoid fever
Typhoid fever is an infection that causes diarrhea and a rash. It is most commonly caused by bacteria called Salmonella typhi (S typhi). S typhi is spread through contaminated food, drink, or water.
Typhoid fever Causes:
If you eat or drink something that is contaminated with the bacteria, the bacteria enter your body. They travel into your intestines, and then into your blood. In the blood, they travel to your lymph nodes, gallbladder, liver, spleen, and other parts of the body.
Some people become carriers of S typhi and continue to release the bacteria in their stools for years, spreading the disease.
Typhoid fever is common in developing countries. Most cases in the United States are brought in from other countries where typhoid fever is common.
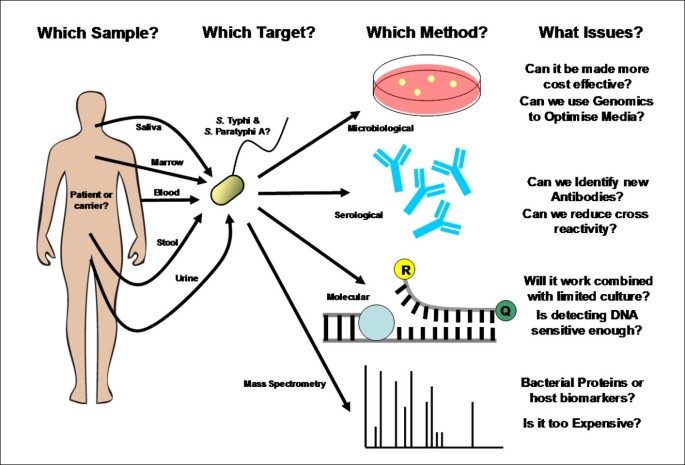
Current typhoid diagnostics
According to the World Health Organization, a definitive diagnosis of typhoid requires isolation of the Salmonella Typhi bacterium through blood culture. This method is considered the gold standard for typhoid diagnosis, though it still has serious practical limitations. Blood cultures are expensive and require specialized personnel and laboratory facilities to perform.
Blood culture facilities are rare in many low-resource countries and are often limited to major hospitals in large cities. When it is possible to perform a blood culture, only 40 to 60 percent of typhoid cases are correctly identified due to the low levels of bacteria in the blood during illness. The best time to test is the early days of infection, but the incubation period means that the highest levels of bacteria in the blood are likely present before clinical symptoms develop. The patient’s prior use of antibiotics as well as the volume of blood collected for the sample also affect the accuracy of blood culture. Furthermore, results are not available until several days after the blood is taken, limiting the test’s usefulness in a clinical setting where a healthcare worker must make a decision about treatment quickly. The development of a more cost-effective, rapid diagnostic test is needed to help avoid misdiagnosis.
Because of these limitations, the diagnosis of typhoid in most low-resource settings is made based on clinical criteria, which is challenging due to the non specificity of typhoid symptoms. Because typhoid symptoms are common to many other illnesses such as malaria and dengue, patients are frequently misdiagnosed. Difficulties with accurate typhoid diagnostics and appropriate treatment can lead to more serious complications and can contribute to drug resistance. Additional methods include urine or stool culture, which, while easier and cheaper to perform, do not have reliable accuracy. The Widal test, developed in the late 1800s, is simple and inexpensive, but it should not be used for diagnosis alone as it is frequently inaccurate due to cross-reactivity with other infectious agents.
Body fluid or tissue culture

For the culture, a small sample of your blood, stool, urine or bone marrow is placed on a special medium that encourages the growth of bacteria. The culture is checked under a microscope for the presence of typhoid bacteria. A bone marrow culture often is the most sensitive test for Salmonella typhi.
Although performing a culture test is the most common diagnostic test, other testing may be used to confirm a suspected typhoid fever infection, such as a test to detect antibodies to typhoid bacteria in your blood, or a test that checks for typhoid DNA in your blood.
Treatment
Antibiotic therapy is the only effective treatment for typhoid fever.
Commonly prescribed antibiotics
Commonly prescribed antibiotics include:
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro). In the United States, doctors often prescribe this for adults who aren’t pregnant. Another similar drug called ofloxacin also may be used. Unfortunately, many Salmonella typhi bacteria are no longer susceptible to antibiotics of this type, particularly strains picked up in Southeast Asia.
- Azithromycin (Zithromax). This may be used if a person is unable to take ciprofloxacin or the bacteria are resistant to ciprofloxacin.
- Ceftriaxone. This injectable antibiotic is an alternative in more-complicated or serious infections and for people who may not be candidates for ciprofloxacin, such as children.
These drugs can cause side effects, and long-term use can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Problems with antibiotic resistance

In the past, the drug of choice was chloramphenicol. Doctors no longer commonly use it because of side effects, a high rate of health deterioration after a period of improvement (relapse) and widespread bacterial resistance.
In fact, antibiotic-resistant bacteria are becoming more common, especially in the developing world. In recent years, Salmonella typhi has also proved resistant to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ampicillin and ciprofloxacin.
Other treatments
Other treatments include:
- Drinking fluids. This helps prevent the dehydration that results from a prolonged fever and diarrhea. If you’re severely dehydrated, you may need to receive fluids through a vein (intravenously).
- Surgery. If your intestines become torn, you’ll need surgery to repair the hole.
Information to gather in advance
- Pre-appointment restrictions. At the time you make your appointment, ask if there are restrictions you need to follow in the time leading up to your visit. Your doctor will not be able to confirm typhoid fever without a blood test, and may recommend taking steps to reduce the risk of passing a possible contagious illness to others.
- Symptom history. Write down any symptoms you’re experiencing and for how long.
- Recent exposure to possible sources of infection. Be prepared to describe international trips in detail, including the countries you visited and the dates you traveled.
- Medical history. Make a list of your key medical information, including other conditions for which you’re being treated and any medications, vitamins or supplements you’re taking. Your doctor will also need to know your vaccination history.
- Questions to ask your doctor. Write down your questions in advance so that you can make the most of your time with your doctor.
For typhoid fever, possible questions to ask your doctor include:
- What are the possible causes for my symptoms?
- What kinds of tests do I need?
- Are treatments available to help me recover?
- I have other health problems. How can I best manage these conditions together?
- How long do you expect a full recovery will take?
- When can I return to work or school?
- Am I at risk of any long-term complications from typhoid fever?
Don’t hesitate to ask any other related questions you have.
What to expect from your doctor
Your doctor is likely to ask you a number of questions. Being ready to answer them may reserve time to go over any points you want to talk about in-depth. Your doctor may ask:
- What are your symptoms and when did they begin?
- Have your symptoms gotten better or worse?
- Did your symptoms briefly get better and then come back?
- Have you recently traveled abroad? Where?
- Did you update your vaccinations before traveling?
- Are you being treated for any other medical conditions?
- Are you currently taking any medications?


[…] Fever or low temperature […]
[…] FeverHeadacheMuscle aches and joint painRashSore throat and painful mouth soresSwollen lymph glands, mainly on the neckDiarrheaWeight lossCoughNight sweatsThese symptoms can be so mild that you might not even notice them. However, the amount of virus in your bloodstream (viral load) is quite high at this time. As a result, the infection spreads more easily during primary infection than during the next stage. […]
[…] Test reveals the presence of salmonella bacteria. Salmonella is actually an intestinal dieses. This fever does not touch normal fever but keeps going up and down. This fever also called step ladder fever. […]
[…] may also experience a mild headache body aches or a Low grade fever. Typically a cold tests 2-14 […]
I think other site proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and wonderful user friendly style and design, let alone the content. You are an expert in this topic!
[…] Fever […]